Built-in guest account not renamed at windows target system – Built-in guest accounts in Windows target systems provide convenient access for temporary users, but they also pose potential security risks. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of managing guest accounts, addressing the importance of strong password policies, remote access considerations, and troubleshooting common issues.
Understanding the security implications and best practices associated with guest accounts is crucial for maintaining a robust and secure system.
System Configuration Overview

The built-in guest account in Windows operating systems is a default user account that provides limited access to the system. It is intended for temporary use by non-regular users, such as visitors or guests who need to access the computer but do not require a permanent account.
Using the default guest account can pose security risks, as it typically has minimal password protection and may grant access to sensitive system resources. To mitigate these risks, it is recommended to rename or disable the guest account and create separate user accounts with appropriate access privileges for each user.
Guest Account Management, Built-in guest account not renamed at windows target system
To rename the built-in guest account in Windows target systems, follow these steps:
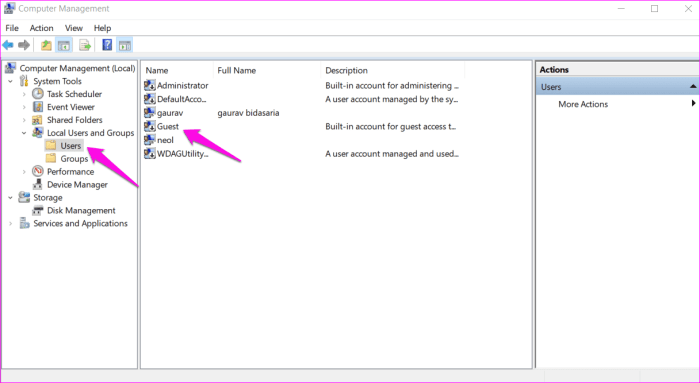
- Open the Computer Management console (compmgmt.msc).
- Navigate to Local Users and Groups > Users.
- Right-click on the Guest account and select Rename.
- Enter the new name for the guest account and click OK.
To disable or delete the guest account, follow these steps:
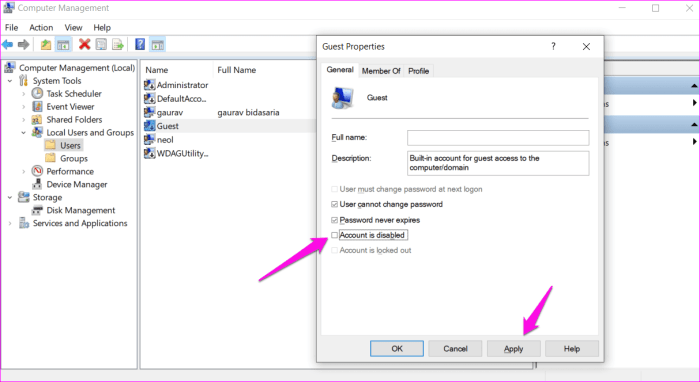
- Open the Computer Management console (compmgmt.msc).
- Navigate to Local Users and Groups > Users.
- Right-click on the Guest account and select Disable Account or Delete.
- Confirm the action and click OK.
In a multi-user environment, it is best practice to create separate user accounts for each user and assign appropriate access privileges to each account. This allows for better control over system access and security.
Troubleshooting and Recovery
If you encounter issues when renaming or managing the guest account, consider the following:
- Ensure that you have administrative privileges.
- Check the User Account Control (UAC) settings and ensure that you are prompted for confirmation when making changes to user accounts.
- Verify that the guest account is not being used by any active processes or applications.
If the guest account becomes inaccessible or corrupted, you can recover or reset it using the following steps:
- Boot into Safe Mode.
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type the following command: net user guest /active:yes
- Press Enter and restart the computer.
Security Considerations
Strong password policies are crucial for guest accounts. Set a complex password and avoid using common or easily guessable passwords.
Allowing remote access to guest accounts can pose security risks. Consider disabling remote access for guest accounts or implementing additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication.
Implement additional security measures to protect guest accounts, such as limiting access to specific applications or folders, and monitoring guest account activity.
Comparison with Other Operating Systems
Compared to macOS, Windows guest accounts have more limited functionality and are typically not enabled by default. In macOS, guest accounts have a separate home directory and can be customized with specific access privileges.
In Linux, guest accounts are typically created and managed through the command line. Linux guest accounts have similar capabilities to Windows guest accounts, but they can be configured with more granular access controls.
Question & Answer Hub: Built-in Guest Account Not Renamed At Windows Target System
Why is it important to rename the built-in guest account?
Renaming the built-in guest account enhances security by making it less predictable and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
What are the potential risks of using the default guest account?
The default guest account has weak security settings, making it vulnerable to attacks and malware infections.
How can I disable or delete the guest account?
To disable the guest account, go to User Accounts in Control Panel and uncheck the box next to “Turn on guest account.” To delete the account, use the command “net user guest /delete” in Command Prompt.